Research Article - (2021) Volume 12, Issue 12
Overuse of Steroid Drugs Methylprednisolone and Dexamethasone (Oral) Causes a Diabetic Patient to Become Infected with the Black Fungus in the Corona Virus
Ashwin Singh Chouhan*, Bharat Parihar, Bharti Rathod and Ramprasad PrajapatAbstract
Background: Overuse of both methylprednisolone and dexamethasone drugs on a corona patient can result in serious side effects and new infections may appear during their use. Infection with any pathogen, including viral, bacterial, fungal, protozoan, or helminthic infections at any site of the body, may be associated with the use of methylprednisolone or dexamethasone in combination with other immunosuppressive agents that increase cellular immunity, humoral immunity, or Suppress neutrophils. The function they affect.
These infections can be mild, but can be serious and sometimes fatal. Overuse doses of methylprednisolone and dexamethasone, the rate of occurrence of infectious complications increases. When methylprednisolone and dexamethasone are used, there may be reduced resistance an inability to localize the infection.
Prolonged use of methylprednisolone and dexamethasone may produce posterior subcapsular glaucoma, glaucoma with potential damage to the optic nerves; it may accelerate the establishment of secondary ocular infections caused by fungi or viruses.
It has also been observed that more methylprednisolone and dexamethasone drugs increases the level of glucose in the body, leading to normal corona patients who do not have any disease and diabetes after recovering from excessive consumption of methylprednisolone and dexamethasone drugs.
Materials and methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted among 50 COVID doctors from the department's outpatient pool of COVID patients, distributing questionnaires to all subjects of different age groups. The questionnaire included information related to the name, age, gender and various factors that affect the doctor's choice of methylprednisolone and dexamethasone.
Result and discussion: A total of 50 doctors and some medical stores from across India were included in the survey. Doctors prescribed more methylprednisolone and dexamethasone medicine than steroid medicines to corona patients. In our research, most side effects were observed for corona patients taking methylprednisolone and dexamethasone drugs.
Conclusion: This research had shown that overdose of methylprednisolone and dexamethasone drugs take diabetes patient he has serious eye effect and causes black fungus.
Keywords
Methylprednisolone, Dexamethasone, Side effect, Drug interaction, Diabetes patients, Black fungus, Eye diseases
Introduction
Methylprednisolone (Depo-Medrol, Medrol, Solu-Medrol) is a synthetic glucocorticoid, primarily prescribed for its anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects (Katzung BG, et al., 2004; Timmermans S, et al., 2019; Xavier AM, et al., 2016). It is either used at low doses for chronic illnesses or used concomitantly at high doses during acute flares. Methylprednisolone and its derivatives can be administered orally or parenterally (Ocejo A and Correa R, 2020).
Regardless of the route of administration, methylprednisolone integrates systemically as exhibited by its effectiveness to quickly reduce inflammation during acute flares (Habib GS, 2009). It is associated with many adverse reactions that require tapering off the drug as soon as the disease is under control (Paragliola RM, et al., 2017). Serious side effects include iatrogenic Cushing's syndrome, hypertension, osteoporosis, diabetes, infection, and skin atrophy (Paragliola RM, et al., 2017).
Chemically, methylprednisolone is a synthetic pregnane steroid hormone derived from hydrocortisone and prednisolone. It belongs to a class of synthetic glucocorticoids and, more generally, corticosteroids. It acts as a mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptor agonist. In compared to other exogenous glucocorticoids, methylprednisolone has a higher affinity to glucocorticoid receptors than to mineralocorticoid receptors.
Glucocorticoid's name was derived after the discovery of their involvement in regulating carbohydrate metabolism (Paragliola RM, et al., 2017). The cellular functions of glucocorticoids, such as methylprednisolone, are now understood to regulate homeostasis, metabolism, development, cognition, and inflammation (Paragliola RM, et al., 2017). They play a critical role in adapting and responding to environmental, physical and emotional stress (Paragliola RM, et al., 2017).
Methylprednisolone was first synthesized and manufactured by The Upjohn Company (now Pfizer) and FDA approved in the United States on October 2, 1957 (US Food and Drug Administration, 2020). In 2018, it was the 153rd most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 4 million prescriptions (ClinCalc, 2021; ClinCalc, 2021). Methylprednisolone has been a prescribed therapy amidst the COVID-19 pandemic, but there is no evidence it is either safe or effective for this purpose (Kosaka M, et al., 2021; Yousefifard M, et al., 2020).
Dexamethasone is a glucocorticoid medication used to treat rheumatic problems, a number of skin diseases, severe allergies, asthma, chronic obstructive lung disease, croup, brain swelling, eye pain following eye surgery, and along with antibiotics in tuberculosis (Dexamethasone, 2017).
In adrenocortical insufficiency, it may be used in combination with a mineralocorticoid medication such as fludrocortisone (Dexamethasone, 2017). In preterm labor, it may be used to improve outcomes in the baby (Dexamethasone, 2017). It may be given by mouth, as an injection into a muscle, as an injection into a vein, as a topical cream or ointment for the skin or as a topical ophthalmic solution to the eye (Dexamethasone, 2017). The effects of dexamethasone are frequently seen within a day and last for about three days (Dexamethasone, 2017).
The long-term use of dexamethasone may result in thrush, bone loss, cataracts, easy bruising, or muscle weakness (Dexamethasone, 2017). It is in pregnancy category C in the United States, meaning that it should only be used when the benefits are predicted to be greater than the risks (Dexamethasone, 2017). In Australia, the oral use is category A, meaning it has been frequently used in pregnancy and not been found to cause problems to the baby (Department of Health, 2014). It should not be taken when breastfeeding (Dexamethasone, 2017).
Dexamethasone has anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressant effects (Dexamethasone, 2017).
Dexamethasone was first synthesized in 1957 by Philip Showalter Hench and was approved for medical use in 1961 (Targetcivils, 2020; Rankovic Z, et al., 2012; Fischer J and Ganellin CR). It is on the World Health Organization's list of essential medicines (World Health Organization, 2019). In 2017, it was the 321st most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than one million prescriptions (ClinCalc, 2021).
Aim
To study the factors that influence doctor’s choice of methylprednisolone and dexamethasone and to understand the most preferred options in selection with respect to the methylprednisolone and dexamethasone.
Materials and Methods
A cross sectional study was conducted among 50 COVID doctor from the outpatient pool of Department of COVID patients were briefed about the study and informed consent was obtained from them and ethical committee approval was obtained from the University. Questionnaires were distributed to all subjects of various age groups. The questionnaire included information related to the COVID patient’s name, age, gender and various factors that influence a doctor’s choice of methylprednisolone and dexamethasone.
Medrol tablets contain methylprednisolone which is a glucocorticoid. Glucocorticoids are adrenocortical steroids, both naturally occurring and synthetic, which are readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Methylprednisolone occurs as a white to practically white, odorless, crystalline powder. It is sparingly soluble in alcohol, in dioxane, and in methanol, slightly soluble in acetone, and in chloroform, and very slightly soluble in ether. It is practically insoluble in water.
The chemical name for methylprednisolone is pregna-1, 4-diene-3, 20-dione, 11, 17, 21-trihydroxy-6-methyl-(6 α, and 11 β)-and the molecular weight is 374.48. The structural for-mula is represented below (Figure 1).
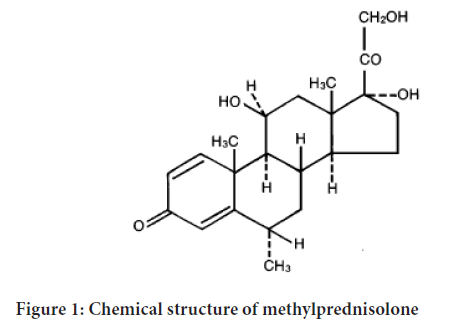
Figure 1: Chemical structure of methylprednisolone
Each medrol (methylprednisolone) Tablet for oral administration contains 2 mg, 4 mg, 8 mg, 16 mg or 32 mg of methylprednisolone.
Dexamethasone, a synthetic adrenocortical steroid, is a white to practically white, odorless, crystalline powder. It is stable in air. It is practically insoluble in water. The molecular formula is C22H29FO5. The molecular weight is 392.47. It is designated chemically as 9-fluoro-11 β, 17, 21-trihydroxy-16 α-methylpregna-1, 4-diene, 3, 20-dione and the structural formula is Figure 2.
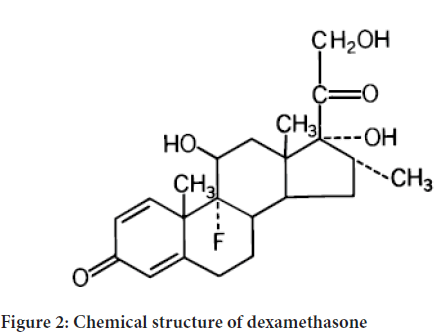
Figure 2: Chemical structure of dexamethasone
Dexamethasone provides relief for inflamed areas of the body. It is used to treat a number of different conditions, such as inflammation (swelling), severe allergies, adrenal problems, arthritis, asthma, blood or bone marrow problems, kidney problems, skin conditions, and flare-ups of multiple sclerosis. Dexamethasone is a corticosteroid (cortisone-like medicine or steroid). It works on the immune system to help relieve swelling, redness, itching, and allergic reactions.
Side effects of methylprednisolone
• Fluid and electrolyte disturbances: Sodium retention, Congestive heart failure in susceptible patients, Hypertension, Fluid retention, Potassium loss, Hypokalemic alkalosis etc.
• Musculoskeletal: Muscle weakness, Loss of muscle mass, Steroid myopathy, Osteoporosis, Tendon rupture, particularly of the Achilles tendon, Vertebral compression fractures, Aseptic necrosis of femoral and humeral heads, Pathologic fracture of long bones etc.
• Gastrointestinal: Peptic ulcer with possible perforation and hemorrhage, Pancreatitis, Abdominal distention, Ulcerative esophagitis, Increases in Alanine Transaminase (ALT, SGPT), Aspartate Transaminase (AST, SGOT), and alkaline phosphatase have been observed following corticosteroid treatment. These changes are usually small, not associated with any clinical syndrome and are reversible upon discontinuation etc.
• Dermatologic: Impaired wound healing Petechiae and ecchymoses, May suppress reactions to skin tests, Thin fragile skin, Facial erythema, Increased sweating etc.
• Neurological: Increased intracranial pressure with papilledema (pseudo- tumor cerebri) usually after treatment, Convulsions, Vertigo, Headache etc.
• Endocrine: Development of Cushingoid state, Suppression of growth in children, Secondary adrenocortical and pituitary unresponsiveness, particularly in times of stress, as in, trauma, surgery or illness, Menstrual irregularities, Decreased carbohydrate tolerance.
• Manifestations of latent diabetes mellitus: Increased requirements of insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents in diabetics
• Ophthalmic: Posterior subcapsular cataracts, Increased intraocular pressure, Glaucoma, Exophthalmos
• Metabolic: Negative nitrogen balance due to protein catabolism
The following additional reactions have been reported following oral as well as parenteral therapy: Urticaria and other allergic, anaphylactic or hypersensitivity reactions (Rxlist, 2020).
Side effects of dexamethasone
The following side effects have been reported with dexamethasone or other corticosteroids:
Allergic reactions: Anaphylactoid reaction, anaphylaxis, angioedema.
Cardiovascular: Bracardia, cardiac arrest, cardiac arrhythmias, cardiac enlargement, circulatory collapse, congestive heart failure, fat embolism, hypertension, hypertrophic, cardiomyopathy in premature infants, myocardial rupture following recent myocardial infarction, edema, pulmonary edema, syncope, tachycardia, thromboembolism, thrombophlebitis, vasculitis etc.
Dermatologic: Acne, allergic dermatitis, dry scaly skin, ecchymoses and petechiae, erythema, impaired wound healing, increased sweating, rash, striae, suppression of reactions to skin tests, thin fragile skin, thinning scalp hair, urticaria etc.
Endocrine: Decrease carbohydrate and glucose tolerance, development of cushingoid state, hyperglycemia, glycosuria, hirsutism, hypertrichosis, increased requirements for insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents in diabetes, manifestations of latent diabetes mellitus, menstrual irregularities, secondary adrenocortical and pituitary unresponsiveness (particularly in times of stress, as in trauma, surgery, or illness), suppression of growth in pediatric patients.
Fluid and electrolyte disturbances: Congestive heart failure in susceptible patient’s fluid retention, hypokalemic alkalosis, potassium loss, sodium retention etc.
Gastrointestinal: Abdominal distention, elevation in serum liver enzyme levels (usually reversible upon discontinuation), hepatomegaly, increased appetite, nausea, pancreatitis, peptic ulcer with possible perforation and hemorrhage, perforation of the small and large intestine (particularly in patients with inflammatory bowel disease), ulcerative esophagitis.
Metabolic: Negative nitrogen balance due to protein catabolism.
Musculoskeletal: Aseptic necrosis of femoral and humeral heads, loss of muscle mass, muscle weakness, osteoporosis, and pathologic fracture of long bones, steroid myopathy, tenson rupture, and vertebral compression fractures.
Neurological/Psychiatric: Convulsions, depression, emotional instability, euphoria, headache, increased intracranial pressure with papilledema (pseudotumor cerebri) usually following discontinuation of treatment, insomnia, mood swings, neuritis, neuropathy, paresthesia, personality changes, psychic disorders, vertigo etc.
Ophthalmic: Exophthalmos, glaucoma, increased intraocular pressure, posterior subcapsular cataracts (Cunha JP, 2020).
Drugs Interaction
Decadron may interact with aminoglutethimide, potassium-depleting agents (e.g., Amphotericin B, diuretics), macrolide antibiotics, anticholinesterases, oral anticoagulants, antidiabetics, antitubercular drugs, cholestyramine, cyclosporine, Dexamethasone Suppression Tests (DST), digitalis glycosides, ephedrine, estrogens and oral contraceptives, barbiturates, phenytoin, carbamazepine, rifampin, ketoconazole, aspirin or other nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs), phenytoin, skin tests, thalidomide, and live or inactivated vaccines. Tell your doctor all medications and supplements you use and all vaccines you recently received. Decadron should be used during pregnancy or during breastfeeding only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus or infant. Infants may suffer adrenal suppression if their mothers use this drug during pregnancy. In special instances (for example, leukemia and nephrotic syndrome), Decadron has been used in pediatric patients. Such use should be done in most patients in conjunction with a pediatric specialist.
Medrol may interact with aspirin (taken on a daily basis or at high doses), diuretics (water pills), blood thinner, cyclosporine, insulin or oral diabetes medications, ketoconazole, rifampin, seizure medications, or "live" vaccines. Tell your doctor all medications and supplements you use and all vaccines you recently received (Fekety R, 1992).
Corticosteroids may mask some signs of infection, and new infections may appear during their use. Infections with any pathogen including viral, bacterial, fungal, protozoan or helminthic infections, in any location of the body, may be associated with the use of corticosteroids alone or in combination with other immunosuppressive agents that affect cellular immunity, humoral immunity, or neutrophil function (Stuck AE, et al., 1989).
These infections may be mild, but can be severe and at times fatal. With increasing doses of corticosteroids, the rate of occurrence of infectious complications increases (Medicover, 2021). There may be decreased resistance and inability to localize infection when corticosteroids are used.
Prolonged use of corticosteroids may produce posterior subcapsular cataracts, glaucoma with possible damage to the optic nerves, and may enhance the establishment of secondary ocular infections due to fungi or viruses.
Black Fungus Infection (Mucormycosis)
• Black fungus, also known as Mucormycosis, is a rare but dangerous infection. Black fungus is caused by getting into contact with fungus spores in the environment. It can also form in the skin after the fungus enters through a cut, scrape, burn, or another type of skin trauma.
• Fungi live in the environment, particularly in soil and decaying organic matter such as leaves, compost piles, rotten wood, and so on. This fungal infection is caused by a type of mould known as 'mucromycetes’. It should be noted that this rare fungal infection affects persons who have health issues or who use drugs that weaken the body's ability to fight the infections (Rxlist, 2020).
Black fungus causes
• Mucormycetes are a type of mould that causes fungal infections. These moulds can be found everywhere in the environment, including soil, air, and food. They enter the body via the nose, mouth, or eyes and can have an impact on the brain if it is not treated on time. According to medical experts, the main cause of black fungus (mucormycosis) is steroid overuse during COVID treatment.
• Black fungus (mucormycosis) primarily affects people who have health problems or who take medications that reduce the body's ability to fight germs and illness. The person's immunity is low after COVID treatment, which makes them vulnerable to black fungus infection. People with diabetes and COVID-19 patients are at greater risk of developing an infection (Rxlist, 2020).
Black fungus risks
People who fall into the following categories are more likely to develop black fungus:
• Uncontrolled diabetes, diabetic ketoacidosis, and diabetics taking steroids or tocilizumab.
• Patients taking immunosuppressant’s or receiving anticancer treatment, as well as those suffering from a chronic debilitating illness
• Patients taking high doses of steroids or tocilizumab for an extended period
• Cases of COVID-19 Severity
• Patients on oxygen who required nasal prongs, a mask, or a ventilator support
• Patients who get COVID treatment within six weeks are more likely to develop black fungus (Rxlist, 2020).
Result and Discussion
A total of 50 doctors and some medical stores from across India were included in the survey. Doctors prescribed more methylprednisolone and dexamethasone drug medicine than steroid medicines to corona patients.
In our research, most side effects were observed for corona patients taking methylprednisolone and dexamethasone drug.
Due to over-prescription of doctors, we came to know from other studies that diabetics who were cured of taking methylprednisolone and dexamethasone medicine when they had corona, got a disease called black fungus after some time. And more deaths from black fungus disease were seen in diabetic patients.
We also found in our survey that Methylprednisolone drug is prescribed more by the doctor in corona patients. Compared to methylprednisolone, doctor prescribed dexamethasone drug is less given in corona patients (Figures 3 and 4).
Figure 3: Names of the cities we placed in our survey
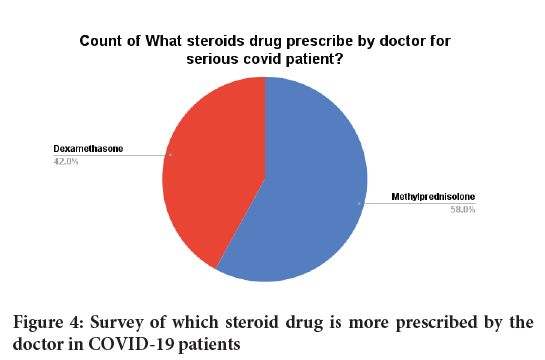
Figure 4: Survey of which steroid drug is more prescribed by the doctor in COVID-19 patients
Conclusion
This research had shown that overdose of methylprednisolone and dexamethasone drug take diabetes patient he has serious eye effect and cause black fungus.
It has been found from research that three things have been detected by giving high amount of steroid drugs to corona patients.
• Patients who have been cured of corona, who did not have any disease before corona, after recovering from corona in their body, after going home, they have diabetes.
• Those corona patients who already have diabetes, after being cured by giving more steroid medicine, they got a complaint of black fungus disease.
• These two things have shown that more steroids are being given to corona patients than giving more side effects because giving more steroids reduces immunity in the body, due to which the black fungus present in the environment is easily found in patients with low immunity. It goes away and the infection increases in the patient's eyes, if the patient does not take treatment on time, then his life is also lost.
However very less work has been on this drug and there is further more scope of scientific investigation.
Acknowledgment
We grateful thanks to all the sincere and extremely helping jai narain vyas university ratanada students for their support and help for the completion of work. Last but not the least, we thankful to all those who cooperated and helped us directly or indirectly to carry out this work.
References
- Katzung BG, Masters SB, Trevor AJ. Basic and clinical pharmacology. McGraw-Hill Medical. 2004.
- Timmermans S, Souffriau J, Libert C. A general introduction to glucocorticoid biology. Front Immunol. 2019; 10: 1545.
- Xavier AM, Anunciato AK, Rosenstock TR, Glezer I. Gene expression control by glucocorticoid receptors during innate immune responses. Front Endocrinol. 2016; 7: 31.
- Ocejo A, Correa R. Methylprednisolone. StatPearls Publishing. 2020.
- Habib GS. Systemic effects of intra-articular corticosteroids. Clin Rheumatol. 2009; 28(7): 749-756.
- Paragliola RM, Papi G, Pontecorvi A, Corsello SM. Treatment with synthetic glucocorticoids and the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis. Int J Mol Sci. 2017; 18(10): 2201.
- US Food and Drug Administration. Drugs@ FDA: FDA-approved drugs. FDA. 2020.
- ClinCalc. The Top 300 of 2021. ClinCalc Drugstat Database. 2021.
- ClinCalc. Methylprednisolone-Drug Usage Statistics. ClinCalc Drugstat Database. 2021.
- Kosaka M, Yamazaki Y, Maruno T, Sakaguchi K, Sawaki S. Corticosteroids as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019: A report of two cases and literature review. J Infect Chemother. 2021; 27(1): 94-98.
- Yousefifard M, Ali KM, Aghaei A, Zali A, Neishaboori AM, Zarghi A, et al. Corticosteroids on the management of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systemic review and meta-analysis. Iran J Public Health. 2020; 49(8): 1411.
- Dexamethasone. The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Drugs. 2017.
- Dexamethasone. Dexamethasone is only recommended for use during pregnancy when there are no alternatives and benefit outweighs risk. Drugs. 2017.
- Department of Health. Prescribing medicines in pregnancy database. Australian Government. 2014.
- Targetcivils. Dexamethasone. Targetcivils. 2020.
- Rankovic Z, Hargreaves R, Bingham M. Drug Discovery for Psychiatric Disorders. Royal Society of Chemistry. 2012.
- Fischer J, Ganellin CR. Analogue-based drug discovery. John Wiley and Sons. 2010; 32(4): 12-15.
- World Health Organization. World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. 2019.
- ClinCalc. Dexamethasone-Drug usage statistics. ClinCalc Drugstat Database. 2021.
- Rxlist. Medrol (methylprednisolone) drug-patient side effects and images. Rxlist. 2020.
- Rxlist. Dexamethasone drug. Rxlist. 2020.
- Rxlist. Dexamethasone side effects drug center. Rxlist. 2020.
- Cunha JP. Decadron vs. Medrol. Rxlist. 2020.
- Fekety R. Infections associated with corticosteroids and immunosuppressive therapy. Infect Dis. 1992; 1050.
- Stuck AE, Minder CE, Frey FJ. Risk of infectious complications in patients taking glucocorticosteroids. Rev Infect Dis. 1989; 11(6): 954-963.
- Medicover. Black Fungus Infection (Mucormycosis). Medicover Hospitals. 2021.
Author Info
Ashwin Singh Chouhan*, Bharat Parihar, Bharti Rathod and Ramprasad PrajapatReceived: 29-Jun-2021 Accepted: 13-Jul-2021 Published: 20-Jul-2021
Copyright: This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ARTICLE TOOLS
- Dental Development between Assisted Reproductive Therapy (Art) and Natural Conceived Children: A Comparative Pilot Study Norzaiti Mohd Kenali, Naimah Hasanah Mohd Fathil, Norbasyirah Bohari, Ahmad Faisal Ismail, Roszaman Ramli SRP. 2020; 11(1): 01-06 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2020.1.01
- Psychometric properties of the World Health Organization Quality of life instrument, short form: Validity in the Vietnamese healthcare context Trung Quang Vo*, Bao Tran Thuy Tran, Ngan Thuy Nguyen, Tram ThiHuyen Nguyen, Thuy Phan Chung Tran SRP. 2020; 11(1): 14-22 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2019.1.3
- A Review of Pharmacoeconomics: the key to “Healthcare for All” Hasamnis AA, Patil SS, Shaik Imam, Narendiran K SRP. 2019; 10(1): s40-s42 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2019.1s.21
- Deuterium Depleted Water as an Adjuvant in Treatment of Cancer Anton Syroeshkin, Olga Levitskaya, Elena Uspenskaya, Tatiana Pleteneva, Daria Romaykina, Daria Ermakova SRP. 2019; 10(1): 112-117 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2019.1.19
- Dental Development between Assisted Reproductive Therapy (Art) and Natural Conceived Children: A Comparative Pilot Study Norzaiti Mohd Kenali, Naimah Hasanah Mohd Fathil, Norbasyirah Bohari, Ahmad Faisal Ismail, Roszaman Ramli SRP. 2020; 11(1): 01-06 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2020.1.01
- Manilkara zapota (L.) Royen Fruit Peel: A Phytochemical and Pharmacological Review Karle Pravin P, Dhawale Shashikant C SRP. 2019; 10(1): 11-14 » doi: 0.5530/srp.2019.1.2
- Pharmacognostic and Phytopharmacological Overview on Bombax ceiba Pankaj Haribhau Chaudhary, Mukund Ganeshrao Tawar SRP. 2019; 10(1): 20-25 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2019.1.4
- A Review of Pharmacoeconomics: the key to “Healthcare for All” Hasamnis AA, Patil SS, Shaik Imam, Narendiran K SRP. 2019; 10(1): s40-s42 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2019.1s.21
- A Prospective Review on Phyto-Pharmacological Aspects of Andrographis paniculata Govindraj Akilandeswari, Arumugam Vijaya Anand, Palanisamy Sampathkumar, Puthamohan Vinayaga Moorthi, Basavaraju Preethi SRP. 2019; 10(1): 15-19 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2019.1.3






